To help you get Python 3 and Python 2 up and running on CentOS 8/Rocky Linux, we’ve put together this detailed installation guide.
It’s no surprise that Python is a widely used programming language. Python’s simple and straightforward syntax makes it a favorite among both inexperienced and seasoned programmers.
CentOS 8/Rocky Linux is not like other Linux distributions in that Python is not pre-installed.
In case you didn’t know, Python comes in not one but two distinct flavors. In 2020, Python 2 will no longer be supported. Python 3 is the cutting edge of programming today and tomorrow.
To prevent users from being locked into a specific version of Python, RHEL/CentOS 8/Rocky Linux does not include an unversioned system-wide python command by default. As an alternative, it allows the user to select which version of Python they would like to use during setup and execution. The internal Python binary and libraries are used by the system tools like yum.
When we say unversioned system-wide, we mean in the terminal.
Unversioned: python
Versioned: python3, python2
Installing Python 3 on CentOS 8/Rocky Linux
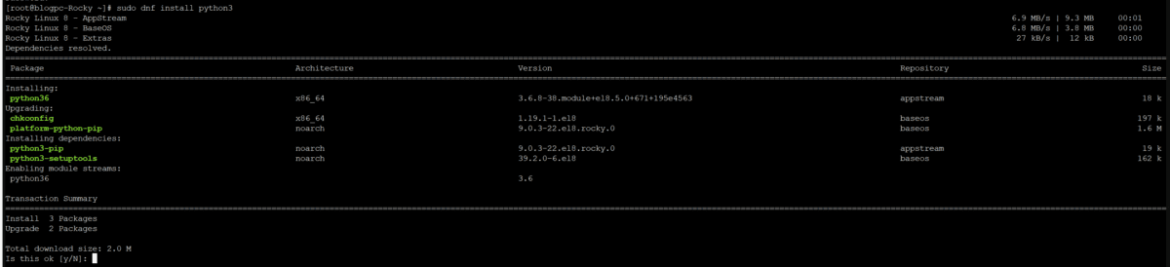
On CentOS 8/Rocky Linux, enter the following command in the terminal as the root or sudo user to install Python 3:
sudo dnf install python3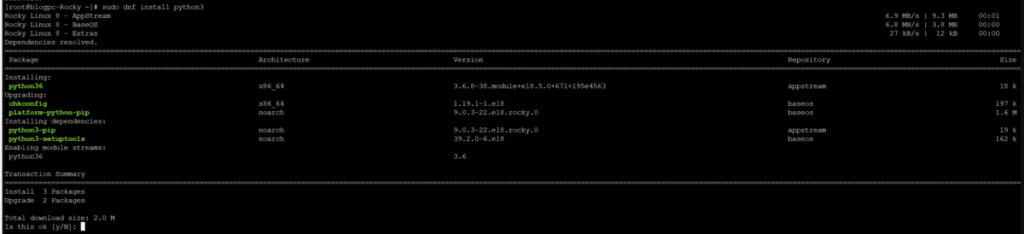
In order to make sure everything is set up properly, you can check the Python version by typing:
python3 --versionAs of this writing, “3.6.x” is the most recent version of Python 3 that can be found in the CentOS repositories:
Python 3.6.8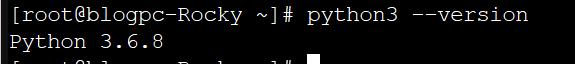
Additionally, pip will be set up with this command.
In order to use Python 3, you must type python3, and to use pip, you must type pip3.
Whenever possible, use yum or dnf to install the python modules that came with your distribution, as these modules have been validated for use with CentOS 8/Rocky Linux and are guaranteed to work properly. Pip should only be used inside of a sandbox. Using Python Virtual Environments, Python modules can be installed locally for use with a single project, rather than globally. There will be no ripple effects on other Python programs.
Python 3 module package names begin with the prefix “python3.” A typical command to install a module would be:
sudo dnf install python3-xyzAs of writing this guide, the latest major release of the Python is 3.8. To install it, you will have to build it from the source .
Installing Python 2 on CentOS 8/Rocky Linux
Python 2 packages are distributed in the official CentOS 8 and Rocky Linux distribution repositories.
Use this command to set up Python 2:
sudo dnf install python2Type in the following to ensure the installation went smoothly:
python2 --versionThe result should resemble this:
Python 2.7.15Python 2 can be run by entering python2, and pip can be launched by typing pip2.
Set Default Python Version (Unversioned Python Command)
The unversioned python command and the default version must be created if any existing programs require the presence of the python command in the system’s path.
Using the alternatives program, you can make Python 3 the default unversioned python command on your entire system:
sudo alternatives --set python /usr/bin/python3When using Python 2, enter:
sudo alternatives --set python /usr/bin/python2Using the alternatives command, a symbolic link named python will be created and pointed to the version of Python you specify.
Enter python —version into the terminal to see the installed version of Python.
Use one of the preceding commands to alter the setup’s default build. Remove the unversioned python command by entering:
sudo alternatives --auto pythonConclusion
Python is not pre-installed on CentOS 8/Rocky Linux.
Python 2 can be installed with dnf install python2, and Python 3 can be installed with dnf install python3.
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to comment below.

1 comment
I admire how you make simpler complicated concepts into manageable and accessible segments.