Redis, which stands for Remote Dictionary Server, is a fast, key-value data store that operates in memory and is free to use. Created by Salvatore Sanfilippo, Redis was initially developed to enhance the scalability of his Italian startup. Today, Redis is a versatile tool used as a database, cache, message broker, and queue.
Why Use Redis with Nextcloud?
Redis is renowned for its impressive response times of less than one millisecond, enabling it to handle millions of requests per second. This makes it an ideal choice for real-time applications in various fields such as gaming, ad-tech, financial services, healthcare, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Its speed and reliability have made Redis one of the most popular open-source engines. For the past five years, it has been named the “Most Loved” database by Stack Overflow.
When integrated with Nextcloud, Redis significantly enhances performance, especially in caching and session management. This optimization is crucial for applications requiring quick data retrieval and processing, such as:
- Caching: Reduces the load on the primary database by storing frequently accessed data.
- Session Management: Ensures fast and reliable user session handling.
- Gaming and Leaderboards: Provides real-time updates and fast data access.
- Real-time Analytics: Delivers immediate insights from live data.
- Geospatial Applications: Handles location-based data efficiently.
- Ride-hailing and Chat/Messaging: Supports high-speed data transactions.
- Media Streaming: Enhances the performance of streaming services.
- Pub/Sub Applications: Efficiently manages publish/subscribe messaging patterns.
Installing Redis on Major Linux Distributions
Most major Linux distributions provide packages for Redis, making installation straightforward. Here’s a quick guide to get you started:
Ubuntu/Debian
For those running a minimal distribution, such as a Docker container or an LXC container, there may be a need to install lsb-release first. This package provides essential information about the Linux distribution in use.
- Machine Used: LXC Container running Ubuntu 20.04
Here’s how you can install lsb-release:
sudo apt install lsb-releaseNote: Installing this package ensures compatibility with various scripts and applications that rely on specific distribution information. It’s particularly useful in containerized environments where such information might not be readily available.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install redis-serverCentOS/RHEL
sudo yum install epel-release
sudo yum install redisFedora
sudo dnf install redis
Remote Access
If you’d like to connect applications that are not on the machine, we can do it this way.
sudo nano /etc/redis/redis.confChange bind 127.0.0.1 to bind 0.0.0.0 . Save and exit and then run:
sudo service redis-server restartPHP-Redis
You’ll need to install the redis php module on the nextcloud server as well:
sudo apt install php-redisStep 2 — Testing Redis for Nextcloud
Prior to making any more changes to Redis’ setup, it’s a good idea to verify that it’s working as intended, as you would with any freshly installed program. We will go through two techniques to confirm that Redis is operating appropriately in this stage.
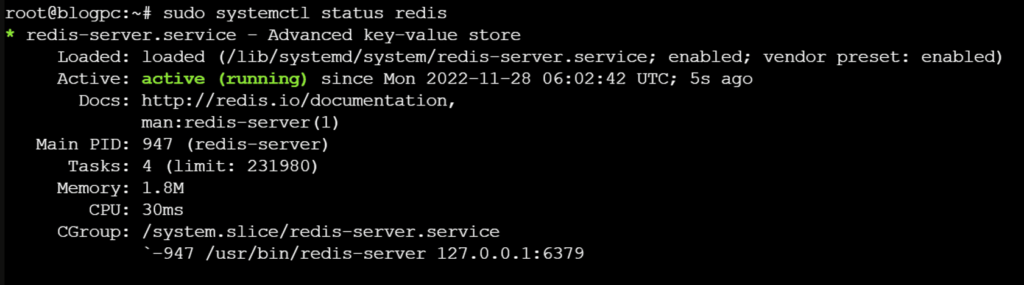
Start by confirming that the Redis service is operating
sudo systemctl status redisIf it is running without any errors, this command will produce output similar to the following:
Connect to the server using redis-cli, the command-line client for Redis, to verify that it is operating properly:
redis-cli
Should be more than enough for testing its connectivity.
Step 3 – Connect Redis to Nextcloud
Local Redis
At this point we know Redis is functional and ready to be implement into our Nextcloud instance. Head to your Nextcloud config folder, edit the config.php and add these lines:
'memcache.local' => '\\OC\\Memcache\\Redis',
'memcache.distributed' => '\\OC\\Memcache\\Redis',
'filelocking.enabled' => 'true',
'memcache.locking' => '\\OC\\Memcache\\Redis',
'redis' =>
array (
'host' => 'localhost',
'port' => 6379,
'timeout' => 0.0,
),Remote Redis server
If you want to use a remote Redis server you need to set the Ip or FQDN of the Redis machine in the ‘host’ parameter:
'memcache.local' => '\\OC\\Memcache\\Redis',
'memcache.distributed' => '\\OC\\Memcache\\Redis',
'filelocking.enabled' => 'true',
'memcache.locking' => '\\OC\\Memcache\\Redis',
'redis' =>
array (
'host' => 'CHANGEME',
'port' => 6379,
'timeout' => 0.0,
),Conclusion
That’s it, your Nextcloud instance should automatically start using Redis for memory caching and help prevent deadlocks.
Optimizing Redis for Nextcloud
After successfully installing Redis and connecting it to your Nextcloud instance, you can further enhance performance by applying various optimization techniques. Below are some essential tips and tuning suggestions to help you make the most out of Redis with Nextcloud.
1. Tuning Redis Configuration
Redis’s performance can be optimized by adjusting its configuration file (/etc/redis/redis.conf). Here are some key settings to consider:
Max Memory
Set a limit on how much memory Redis can use based on your system’s available resources. This prevents Redis from consuming all available system memory and ensures stable performance.
maxmemory 256mb
maxmemory-policy allkeys-lruPersistence Options
Depending on your requirements, you can enable or disable persistence to improve performance. If data persistence is not critical, disabling it can free up I/O resources.
appendonly noTCP Keepalive
Set an appropriate value for TCP keepalive to ensure a more reliable connection.
tcp-keepalive 3002. Monitoring Redis Performance
To maintain optimal performance, it’s crucial to monitor Redis’s behavior and resource usage. Redis provides several tools for this purpose:
Monitoring Commands
Use the redis-cli monitor command to observe all the commands processed by the server in real-time. This helps in identifying any performance bottlenecks.
redis-cli monitorBenchmarking
Run the redis-benchmark tool to test how many requests per second your Redis server can handle. This provides a clear picture of your Redis instance’s performance capabilities.
redis-benchmark3. Securing Redis
If your Redis instance is exposed to the WAN network (e.g., binding to 0.0.0.0 and 1:1 or port forwarding), implementing security measures is crucial to prevent unauthorized access:
Set a Strong Password
Configure a strong password in the Redis configuration file to protect your instance from unauthorized access.
requirepass your-strong-passwordUse Firewall Rules
Ensure that only trusted IP addresses can connect to your Redis port (usually 6379). This can be achieved by configuring your firewall rules accordingly.
For more in-depth instructions and advanced configurations, refer to the official Redis documentation and Nextcloud documentation.

